M. Shevtsov, B. Nikolaev, Y. Marchenko, L. Yakovleva, N.V. Skvorzov, A. Mazur, P. Tolstoy, V. Ryzhov, G. Multhoff
“Targeting experimental orthotopic glioblastoma with chitosan-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (CS-DX-SPIONs)”
Int. J. Nanomedicine, 2018, 13, 1471-1482
DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S152461
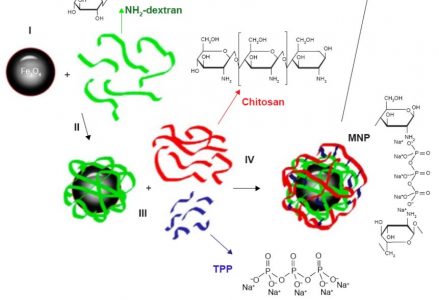
Glioblastoma is the most devastating primary brain tumor of the central nervous system in adults. Magnetic nanocarriers may help not only for a targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into the tumor site but also provide contrast enhancing properties for diagnostics using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)