V.V. Sivchik, E.V. Grachova, A.S. Melnikov, S.N. Smirnov, A.Yu. Ivanov, P.Hirva, S.P. Tunik, I.O. Koshevoy
“Solid-State and Solution Metallophilic Aggregation of a Cationic [Pt(NCN)L]+ Cyclometalated Complex”
Inorg. Chem., 2016, ASAP
DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b02713
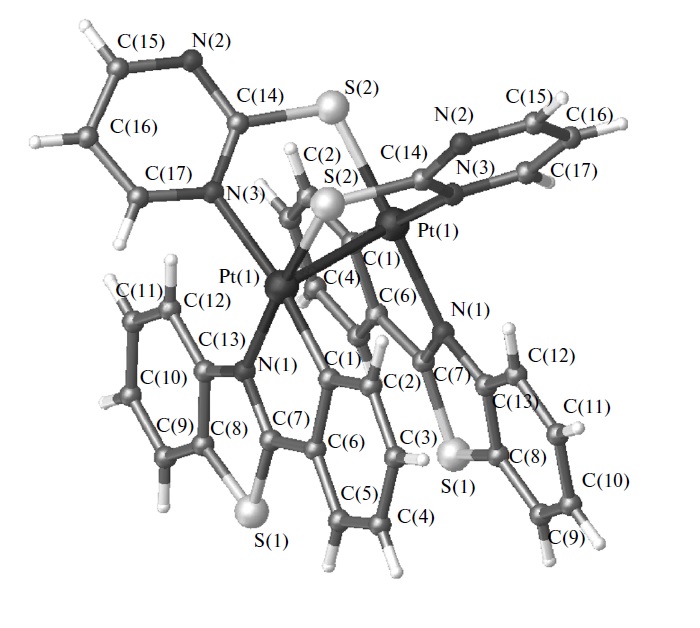
The noncovalent intermolecular interactions (π–π stacking, metallophilic bonding) of the cyclometalated complexes [Pt(NCN)L]+X– (NCN = dipyridylbenzene, L = pyridine (1), acetonitrile (2)) are determined by the steric properties of the ancillary ligands L in the solid state and in solution, while the nature of the counterion X– (X– = PF6–, ClO4–, CF3SO3–) affects the molecular arrangement of 2·X in the crystal medium. According to the variable-temperature X-ray diffraction measurements, the extensive Pt···Pt interactions and π-stacking in 2·X are significantly temperature-dependent. The variable concentration 1H and diffusion coefficients NMR measurements reveal that 2·X exists in the monomeric form in dilute solutions at 298 K, while upon increase in concentration [Pt(NCN)(NCMe)]+ cations undergo the formation of the ground-state oligomeric aggregates with an average aggregation number of ∼3. The photoluminescent characteristics of 1 and 2·X are largely determined by the intermolecular aggregation. For the discrete molecules the emission properties are assigned to metal perturbed IL charge transfer mixed with some MLCT contribution. In the case of oligomers 2·X the luminescence is significantly red-shifted with respect to 1 and originates mainly from the 3MMLCT excited states. The emission energies depend on the structural arrangement in the crystal and on the complex concentration in solution, variation of which allows for the modulation of the emission color from greenish to deep red. In the solid state the lability of the ligands L leads to vapor-induced reversible transformation 1 ↔ 2 that is accompanied by the molecular reorganization and, consequently, dramatic change of the photophysical properties. Time-dependent density functional theory calculations adequately support the models proposed for the rationalization of the experimental observations.