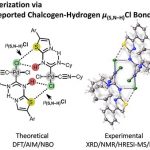
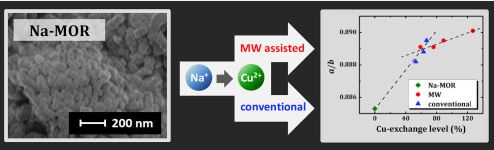
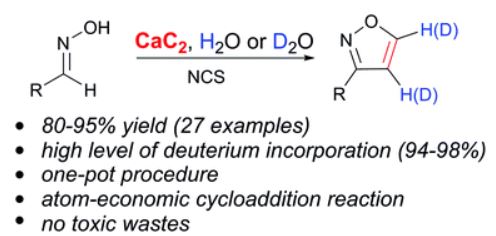
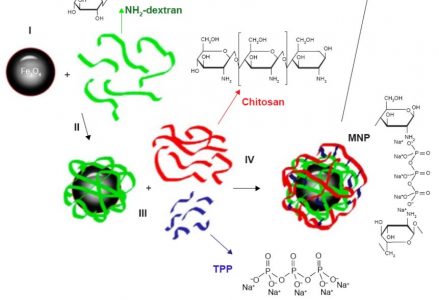
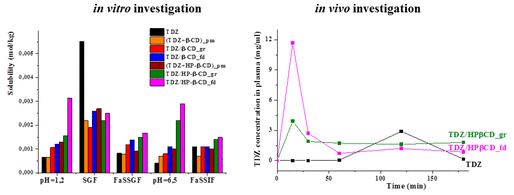
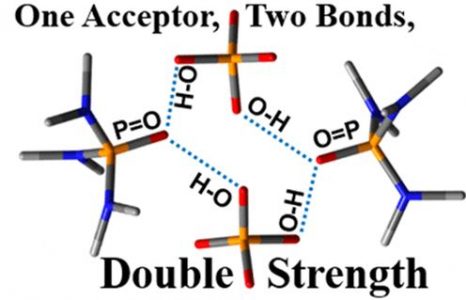
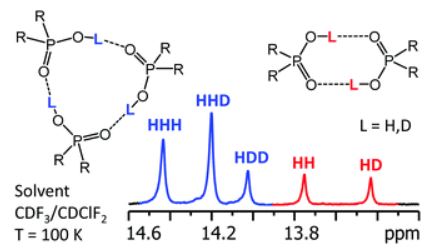
A. S. Mikherdov , A. S. Novikov , M. A. Kinzhalov , V. P. Boyarskiy, G. L. Starova, A. Yu. Ivanov, V. Yu. Kukushkin
“Halides Held by Bifurcated Chalcogen-Hydrogen Bonds. Effect of µ(S,N-H)Cl Contacts on Dimerization of Cl(carbene)PdII Species ”
Inorg. Chem. , 2018, 57(6), 3420-3433
DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b00190
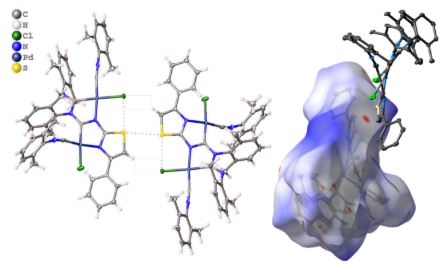
The reaction of cis-[PdCl2(CNCy)2] (1) with thiazol-2-amines (2–10) leads to the C,N-chelated diaminocarbene-like complexes [PdCl{C(N(H)4,5-R2-thiazol-2-yl)NHCy}(CNCy)] (11–14; 82–91%) in the case of 4,5-R2-thiazol-2-amines (R, R = H, H (2), Me, Me (3), −(CH2)4– (4)) and benzothiazol-2-amine (5) or gives the diaminocarbene species cis-[PdCl2{C(N(H)Cy)N(H)4-R-thiazol-2-yl}(CNCy)] (15–19; 73–93%) for the reaction with 4-aryl-substituted thiazol-2-amines (R = Ph (6), 4-MeC6H4 (7), 4-FC6H4 (8), 4-ClC6H4 (9), 3,4-F2C6H3 (10)). Inspection of the single-crystal X-ray diffraction data for 15–17 and 19 suggests that the structures of all these species exhibit previously unrecognized bifurcated chalcogen–hydrogen bonding μ(S,N–H)Cl and also PdII···PdII metallophilic interactions. These noncovalent interactions collectively connect two symmetrically located molecules of 15–17 and 19, resulting in their solid-state dimerization. The existence of the μ(S,N–H)Cl system and its strength (6–9 kcal/mol) were additionally verified/estimated by a Hirshfeld surface analysis and DFT calculations combined with a topological analysis of the electron density distribution within the formalism of Bader’s theory (AIM method) and NBO analysis. The observed noncovalent interactions are jointly responsible for the dimerization of 15–19 not only in the solid phase but also in CHCl3 solutions, as predicted theoretically by DFT calculations and confirmed experimentally by FTIR, HRESI-MS, 1H NMR, and diffusion coefficient NMR measurements. Available CCDC data were processed under the new moiety angle, and the observed μ(S,E–H)Cl systems were classified accordingly to E (E = N, O, C) type atoms.