M.A. Sandzhieva, A.N. Kazakova, I.A. Boyarskaya, A.Yu. Ivanov, V.G. Nenajdenko, A.V. Vasilyev
“Friedel–Crafts Alkylation of Arenes with 2-Halogeno-2-CF3-styrenes under Superacidic Conditions. Access to Trifluoromethylated Ethanes and Ethenes”
J. Org. Chem., 2016, 81, 5032-5045
DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.6b00419
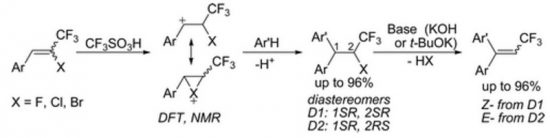
The formation of the corresponding benzyl cations [ArHC+–CH(X)CF3] takes place under protonation of E-/Z-2-halogeno-2-CF3 styrenes [ArCH═C(X)CF3, X = F, Cl, Br] in superacids. The structures of these new electrophiles were studied by means of NMR and theoretical DFT calculations. According to these data, in the case of bromo derivatives, the formed cations, most probably, exist as cyclic bromonium ions; however, in the cases of chloro and fluoro derivatives, open forms are more preferable. Subsequent reaction of these benzyl cations with arenes proceeds as Friedel–Crafts alkylation to afford 1,1-diaryl-2-halo-3,3,3-trifluoropropanes [Ar(Ar′)CH–CH(X)CF3] in high yields (up to 96%) as a mixture of two diastereomers. The prepared halogenopropanes were easily converted into the corresponding mixtures of E-/Z-trifluoromethylated diarylethenes [Ar(Ar′)C═CCF3] (in yields up to 96%) by dehydrohalogenation with base (KOH or t-BuOK). The mechanism of elimination (E2 and Ecb) depends on the nature of the leaving group and reaction conditions.