P.Mäki-Arvela, J.Zhu, N.Kumar, K. Eränen, A.Aho, J.Linden, J.Salonen, M.Peurla, A.Mazur, V.Matveev, D.Y.Murzin
“Solvent-free “green” amidation of stearic acid for synthesis of biologically active alkylamides over iron supported heterogeneous catalysts”
Applied Catalysis: A, 2017, 542, 350-358
DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.06.006
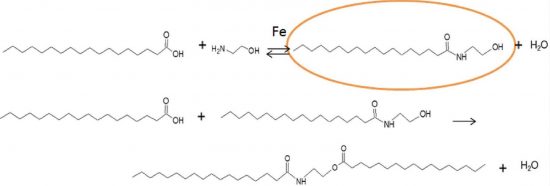
Stearoyl ethanolamine was synthesized by amidation of stearic acid with ethanolamine in solventless conditions. Iron containing heterogeneous catalysts supported on SiO2, Al2O3, Beta (BEA), ZSM-12 (MTW) and Ferrierite (FER) were used in this work. Sn-modified Ferrierite and H-Ferrierite were also studied for comparison. Fe-modified catalysts synthesized using solid state ion-exchange and evaporation impregnation methods, were thoroughly characterized with X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscope, FTIR with pyridine, nitrogen adsorption, energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis and Mössbauer spectroscopy. The highest conversion was obtained with Fe-H-FER-20 at 140 °C in 1 h giving 61% conversion and 98% selectivity towards the desired amide. The catalytic performance in terms of turnover frequency per mole of iron was achieved with the catalyst exhibiting the largest amount of Fe3+ species, optimum acidity and a relatively low Brønsted to Lewis acid site ratio.